Today in Naval History - Naval / Maritime Events in History
Other Events on 23 April
1014 – Battle of Clontarf: High King of Ireland Brian Boru defeats Viking invaders, but is killed in battle.
The Battle of Clontarf (Irish: Cath Chluain Tarbh) was a battle that took place on 23 April 1014 by the River Tolka, from Clontarf inland, near the then-small Dublin. It pitted forces led by Brian Boru, High King of Ireland, against a Norse-Irish alliance comprising the forces of Sigtrygg Silkbeard, King of Dublin; Máel Mórda mac Murchada, King of Leinster; and an external Viking contingent led by Sigurd, of Orkney; and Brodir of Mann. It lasted from sunrise to sunset, and ended in a rout of the Viking and Leinster forces. It is estimated that between 7,000 and 10,000 men were killed. Although Brian's forces were victorious, Brian himself was killed, as were his son Murchad and his grandson Toirdelbach. Leinster king Máel Mórda and Viking leaders Sigurd and Brodir were also slain.

Battle of Clontarf, oil on canvas painting by Hugh Frazer, 1826
After the battle, the Vikings and the Kingdom of Dublin were reduced to a secondary power. Brian's family was temporarily eclipsed, and there was no undisputed High King of Ireland until the late 12th century.
The battle was an important event in Irish history and is recorded in both Irish and Norse chronicles. In Ireland, the battle came to be seen as an event that freed the Irish from foreign domination, and Brian was hailed as a national hero. This view was especially popular during English rule in Ireland. Although the battle has come to be viewed in a more critical light, it still has a hold on the popular imagination.

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
1621 – Birth of William Penn, English admiral and politician (d. 1670)
Sir William Penn (23 April 1621 – 16 September 1670) was an English admiral and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1660 to 1670. He was the father of William Penn, founder of the Province of Pennsylvania.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Penn_(Royal_Navy_officer)
1692 – Launch of HMS Breda was a 70-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Woolwich Dockyard
HMS Breda was a 70-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Woolwich Dockyard on 23 April 1692. She was named after the Declaration of Breda made in 1660 by Charles II of England.
In 1701, under Captain Christopher Fogg, she became the flagship of Vice-Admiral John Benbow. His squadron left for the West Indies on 2 September 1701 as the War of the Spanish Succession began.
During the Action of August 1702, Breda, under Benbow's command, was one of only two ships in the squadron to effectively engage the French. After several days, the contumacy of Benbow's captains in refusing to fight, and his own injuries, forced him to return to Port Royal, where several were convicted of cowardice at a court-martial.
In 1718, Breda was commanded by Captain Barrows Harris, and took part in the Battle of Cape Passaro. During the Blockade of Porto Bello (1726–7) she served as flagship for Vice-Admiral Hosier, who died aboard her in 1727.[3] She was broken up in 1730.

The Battle of Cape Passaro, 11 August 1718 by Richard Paton (oil on canvas, 1767)
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
1750 – Launch of French Rose, (one-off 30-gun design of 1749 by Joseph Chapelle, with 8 x 12-pounders on the lower deck and 22 x 8-pounders (or 6-pounders) on the gun deck; launched 23 April 1750 at Toulon) – sold 1781
1750 – Launch of French Gracieuse, (one-off 24-gun design of 1749 by Joseph Chapelle, with 24 x 12-pounder guns, launched 23 April 1750 at Toulon) – sold 1781.
1768 – Launch of Spanish San Vicente Ferrer 80 (launched 23 April 1768 at Cartagena) - Scuttled 16 February 1797
San Vicente Ferrer Class 80 guns.
San Vicente Ferrer 80 (launched 23 April 1768 at Cartagena) - Scuttled 16 February 1797
San Nicolás Bari 80 (launched 5 April 1769 at Cartagena) - Captured by Britain at the Battle of Cape St Vincent, 14 February 1797, renamed HMS San Nicholas, sold 1814
San Rafael 80 (-) - Destroyed by fire on stocks at Havana 1769
1782 HMS Queen (98), Cptn. Maitland, took Actionnaire (64 flute)
HMS Queen was a three-deck 90-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 18 September 1769 at Woolwich Dockyard. She was designed by William Bateley, and was the only ship built to her draught. Her armament was increased to 98 guns in the 1780s

Scale: 1:48. Plan showing the body plan with sternboard outline, sheer lines with inboard detail, and longitudinal half-breadth for 'Queen' (1769), a 90-gun Second Rate, three-decker, to be built at Woolwich Dockyard. Signed by William Bately [Surveyor of the Navy, 1755-1765]

 en.wikipedia.org
https://collections.rmg.co.uk/colle...el-341486;browseBy=vessel;vesselFacetLetter=Q
en.wikipedia.org
https://collections.rmg.co.uk/colle...el-341486;browseBy=vessel;vesselFacetLetter=Q
1796 – Launch of HMS Termagant was an 18-gun Bittern-class sloop of the Royal Navy.
HMS Termagant was an 18-gun sloop of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1796 and performed convoy duty during the French Revolutionary Wars, shuttling between The Nore and Riga under Commander David Lloyd in mid-1797 in the company of HMS Clyde

Scale: 1:48. Plan showing the body plan, sheer lines and longitudinal half-breadth for Termagant (1796),
 en.wikipedia.org
https://collections.rmg.co.uk/collections.html#!csearch;searchTerm=Termagant_(1796
en.wikipedia.org
https://collections.rmg.co.uk/collections.html#!csearch;searchTerm=Termagant_(1796
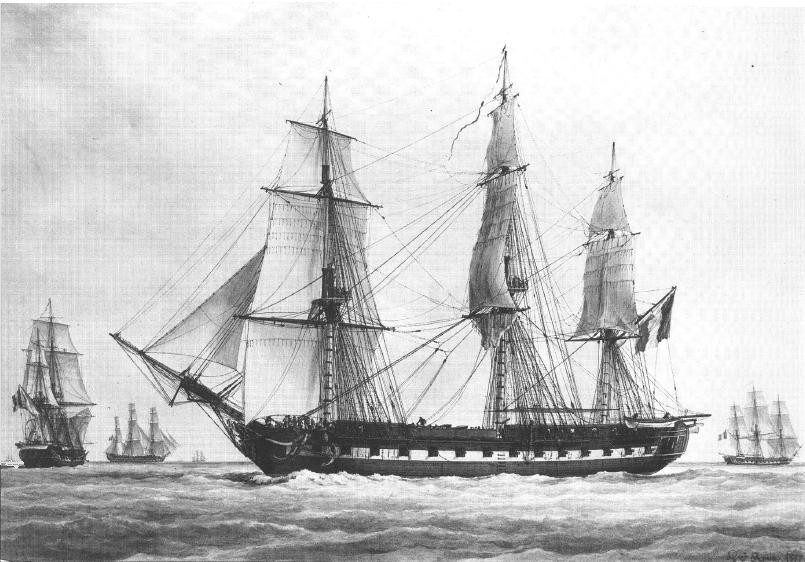
1797 HMS Magicienne (32), Cptn. William Henry Ricketts, HMS Regulus (44), and HMS Fortune (14), took a sloop (6) and four schooners and drove off an attacking force at Careasse Bay, Haiti.
Magicienne was a frigate of the French Navy, lead ship of her class. The British captured her in 1781 and she served with the Royal Navy until her crew burned her in 1810 to prevent her capture after she grounded at Isle de France (now Mauritius). During her service with the Royal Navy she captured several privateers and participated in the Battle of San Domingo.
HMS Regulus (1785) was a wooden fifth rate of 44 guns, launched at Northam in January 1785 and converted to a troopship in 1793. Because Regulus served in the navy's Egyptian campaign (8 March to 2 September 1801), her officers and crew qualified for the clasp "Egypt" to the Naval General Service Medal, which the Admiralty issued in 1847 to all surviving claimants. The ship was broken up in March 1816.
HMS Fortune (1780) was a 14-gun brig-sloop launched in 1780 and wrecked in 1797.

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
1804 - Cuthbert Collingwood promoted to Vice Admiral of the Blue and Horatio Nelson to Vice Admiral of the White

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
1805 - HMS Gallant (14). Lt. Thomas Shirley, and consorts captured eight gun-vessels off Cap Gris Nez.
HMS Gallant (1804) was a 12-gun gun-brig launched in 1804 and sold in 1815.
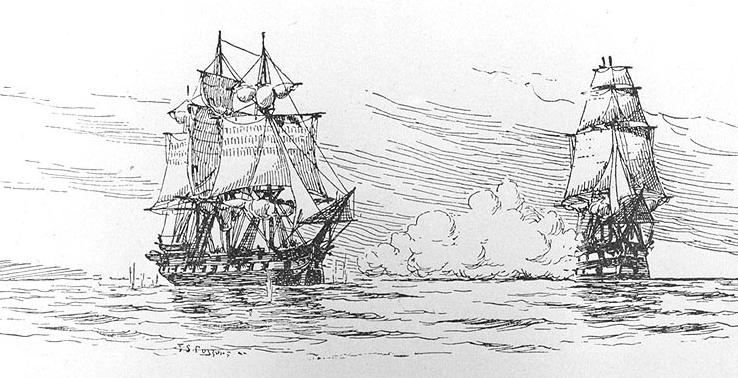
1809 HMS Spartan (38), Cptn. Jahleel Brenton, HMS Amphion (32), Cptn. William Hoste, and HMS Mercury (28), Cptn. Henry Duncan, bombarded Pesaro, took 13 vessels and destroyed a castle.
HMS Spartan was a Royal Navy 38-gun fifth-rate frigate, launched at Rochester in 1806. During the Napoleonic Wars she was active in the Adriatic and in the Ionian Islands. She then moved to the American coast during the War of 1812, where she captured a number of small vessels, including a US Revenue Cutter and a privateer, the Dart. She then returned to the Mediterranean, where she remained for a few years. She went on to serve off the American coast again, and in the Caribbean, before being broken up in 1822.
HMS Mercury was a 28-gun Enterprise-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was built during the American War of Independence and serving during the later years of that conflict. She continued to serve during the years of peace and had an active career during the French Revolutionary Wars and most of the Napoleonic Wars, until being broken up in 1814.

HMS Mercury cutting out a French gunboat from Rovigno, 1 April 1809
HMS Amphion was a 32-gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She served during the Napoleonic Wars.
Amphion was built by Betts, of Mistleythorn, and was launched on 19 March 1798.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Spartan_(1806)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Mercury_(1779)

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
1811 – Launch of HMS Investigator was a survey brig of the Royal Navy
HMS Investigator was a survey brig of the Royal Navy. She performed surveying duties until she was paid off in 1835. She then became a police ship moored on the Thames River. she was broken up in 1857.

Scale: 1:48. Plan showing the body plan with stern board detail, sheer lines with inboard detail, and longitudinal half-breadth for building the Investigator (1811) as a 6-gun Survey Vessel. Signed Henry Peake [Surveyor of the Navy, 1806-1822]
 en.wikipedia.org
https://collections.rmg.co.uk/colle...el-320962;browseBy=vessel;vesselFacetLetter=I
en.wikipedia.org
https://collections.rmg.co.uk/colle...el-320962;browseBy=vessel;vesselFacetLetter=I
1839 – Death of Jacques Félix Emmanuel Hamelin, French admiral and explorer (b. 1768)
Baron Jacques Félix Emmanuel Hamelin (13 October 1768 – 23 April 1839) was a rear admiral of the French navy and later a Baron. He commanded numerous naval expeditions and battles with the British Navy as well as exploratory voyages in the Indian Ocean and the South Seas.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jacques_Félix_Emmanuel_Hamelin
1889 – Birth of Karel Doorman, Dutch admiral (d. 1942)
Karel Willem Frederik Marie Doorman (23 April 1889 – 28 February 1942) was a Dutch naval officer who during World War II commanded remnants of the short-lived American-British-Dutch-Australian Commandnaval strike forces in the Battle of the Java Sea. He was killed in action when his flagship HNLMS De Ruyter was torpedoed during the battle, having chosen to go down with the ship.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karel_Doorman
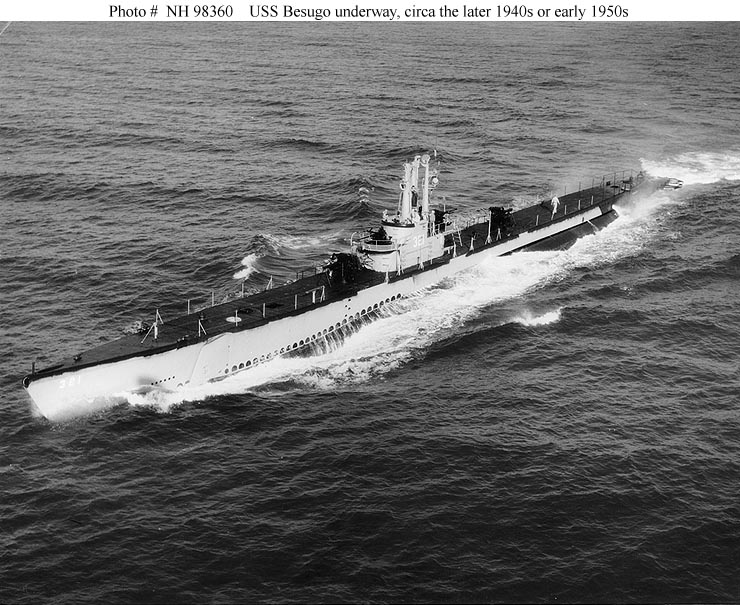
1945 – The Action of 23 April 1945 was a submarine engagement of World War II that occurred in the Java Sea between Nazi Germany and the United States. USS Besugo (SS 321) sinks the German submarine U 183 in the Java Sea.
The Action of 23 April 1945 was a submarine engagement of World War II that occurred in the Java Sea between Nazi Germany and the United States. It resulted in the last sinking of a German U-boat in Asian waters during the Pacific War and was one of only a few actions of the theater involving German forces.
USS Besugo, under the command of Lieutenant Commander Herman Edward Miller, made radar contact with U-183 at about 01:00 off the southern coast of Borneo while patrolling the area. Underwater, the Americans fired a spread of torpedoes and one struck the U-boat which had a Japanese flag painted on the side. The German submarine sank quickly at position 04°50′S 112°52′E with 54 men still aboard, including Kapitänleutnant (Lieutenant Commander) Fritz Schneewind. Afterward, the Americans surfaced and rescued one wounded German warrant officer and took him prisoner.

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
Other Events on 23 April
1014 – Battle of Clontarf: High King of Ireland Brian Boru defeats Viking invaders, but is killed in battle.
The Battle of Clontarf (Irish: Cath Chluain Tarbh) was a battle that took place on 23 April 1014 by the River Tolka, from Clontarf inland, near the then-small Dublin. It pitted forces led by Brian Boru, High King of Ireland, against a Norse-Irish alliance comprising the forces of Sigtrygg Silkbeard, King of Dublin; Máel Mórda mac Murchada, King of Leinster; and an external Viking contingent led by Sigurd, of Orkney; and Brodir of Mann. It lasted from sunrise to sunset, and ended in a rout of the Viking and Leinster forces. It is estimated that between 7,000 and 10,000 men were killed. Although Brian's forces were victorious, Brian himself was killed, as were his son Murchad and his grandson Toirdelbach. Leinster king Máel Mórda and Viking leaders Sigurd and Brodir were also slain.

Battle of Clontarf, oil on canvas painting by Hugh Frazer, 1826
After the battle, the Vikings and the Kingdom of Dublin were reduced to a secondary power. Brian's family was temporarily eclipsed, and there was no undisputed High King of Ireland until the late 12th century.
The battle was an important event in Irish history and is recorded in both Irish and Norse chronicles. In Ireland, the battle came to be seen as an event that freed the Irish from foreign domination, and Brian was hailed as a national hero. This view was especially popular during English rule in Ireland. Although the battle has come to be viewed in a more critical light, it still has a hold on the popular imagination.

Battle of Clontarf - Wikipedia
1621 – Birth of William Penn, English admiral and politician (d. 1670)
Sir William Penn (23 April 1621 – 16 September 1670) was an English admiral and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1660 to 1670. He was the father of William Penn, founder of the Province of Pennsylvania.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Penn_(Royal_Navy_officer)
1692 – Launch of HMS Breda was a 70-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Woolwich Dockyard
HMS Breda was a 70-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Woolwich Dockyard on 23 April 1692. She was named after the Declaration of Breda made in 1660 by Charles II of England.
In 1701, under Captain Christopher Fogg, she became the flagship of Vice-Admiral John Benbow. His squadron left for the West Indies on 2 September 1701 as the War of the Spanish Succession began.
During the Action of August 1702, Breda, under Benbow's command, was one of only two ships in the squadron to effectively engage the French. After several days, the contumacy of Benbow's captains in refusing to fight, and his own injuries, forced him to return to Port Royal, where several were convicted of cowardice at a court-martial.
In 1718, Breda was commanded by Captain Barrows Harris, and took part in the Battle of Cape Passaro. During the Blockade of Porto Bello (1726–7) she served as flagship for Vice-Admiral Hosier, who died aboard her in 1727.[3] She was broken up in 1730.

The Battle of Cape Passaro, 11 August 1718 by Richard Paton (oil on canvas, 1767)
HMS Breda (1692) - Wikipedia
1750 – Launch of French Rose, (one-off 30-gun design of 1749 by Joseph Chapelle, with 8 x 12-pounders on the lower deck and 22 x 8-pounders (or 6-pounders) on the gun deck; launched 23 April 1750 at Toulon) – sold 1781
1750 – Launch of French Gracieuse, (one-off 24-gun design of 1749 by Joseph Chapelle, with 24 x 12-pounder guns, launched 23 April 1750 at Toulon) – sold 1781.
1768 – Launch of Spanish San Vicente Ferrer 80 (launched 23 April 1768 at Cartagena) - Scuttled 16 February 1797
San Vicente Ferrer Class 80 guns.
San Vicente Ferrer 80 (launched 23 April 1768 at Cartagena) - Scuttled 16 February 1797
San Nicolás Bari 80 (launched 5 April 1769 at Cartagena) - Captured by Britain at the Battle of Cape St Vincent, 14 February 1797, renamed HMS San Nicholas, sold 1814
San Rafael 80 (-) - Destroyed by fire on stocks at Havana 1769
1782 HMS Queen (98), Cptn. Maitland, took Actionnaire (64 flute)
HMS Queen was a three-deck 90-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 18 September 1769 at Woolwich Dockyard. She was designed by William Bateley, and was the only ship built to her draught. Her armament was increased to 98 guns in the 1780s

Scale: 1:48. Plan showing the body plan with sternboard outline, sheer lines with inboard detail, and longitudinal half-breadth for 'Queen' (1769), a 90-gun Second Rate, three-decker, to be built at Woolwich Dockyard. Signed by William Bately [Surveyor of the Navy, 1755-1765]

HMS Queen (1769) - Wikipedia
1796 – Launch of HMS Termagant was an 18-gun Bittern-class sloop of the Royal Navy.
HMS Termagant was an 18-gun sloop of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1796 and performed convoy duty during the French Revolutionary Wars, shuttling between The Nore and Riga under Commander David Lloyd in mid-1797 in the company of HMS Clyde

Scale: 1:48. Plan showing the body plan, sheer lines and longitudinal half-breadth for Termagant (1796),
HMS Termagant (1796) - Wikipedia
1797 HMS Magicienne (32), Cptn. William Henry Ricketts, HMS Regulus (44), and HMS Fortune (14), took a sloop (6) and four schooners and drove off an attacking force at Careasse Bay, Haiti.
Magicienne was a frigate of the French Navy, lead ship of her class. The British captured her in 1781 and she served with the Royal Navy until her crew burned her in 1810 to prevent her capture after she grounded at Isle de France (now Mauritius). During her service with the Royal Navy she captured several privateers and participated in the Battle of San Domingo.
HMS Regulus (1785) was a wooden fifth rate of 44 guns, launched at Northam in January 1785 and converted to a troopship in 1793. Because Regulus served in the navy's Egyptian campaign (8 March to 2 September 1801), her officers and crew qualified for the clasp "Egypt" to the Naval General Service Medal, which the Admiralty issued in 1847 to all surviving claimants. The ship was broken up in March 1816.
HMS Fortune (1780) was a 14-gun brig-sloop launched in 1780 and wrecked in 1797.

French frigate Magicienne (1778) - Wikipedia
1804 - Cuthbert Collingwood promoted to Vice Admiral of the Blue and Horatio Nelson to Vice Admiral of the White

Cuthbert Collingwood, 1st Baron Collingwood - Wikipedia

Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson - Wikipedia
1805 - HMS Gallant (14). Lt. Thomas Shirley, and consorts captured eight gun-vessels off Cap Gris Nez.
HMS Gallant (1804) was a 12-gun gun-brig launched in 1804 and sold in 1815.
1809 HMS Spartan (38), Cptn. Jahleel Brenton, HMS Amphion (32), Cptn. William Hoste, and HMS Mercury (28), Cptn. Henry Duncan, bombarded Pesaro, took 13 vessels and destroyed a castle.
HMS Spartan was a Royal Navy 38-gun fifth-rate frigate, launched at Rochester in 1806. During the Napoleonic Wars she was active in the Adriatic and in the Ionian Islands. She then moved to the American coast during the War of 1812, where she captured a number of small vessels, including a US Revenue Cutter and a privateer, the Dart. She then returned to the Mediterranean, where she remained for a few years. She went on to serve off the American coast again, and in the Caribbean, before being broken up in 1822.
HMS Mercury was a 28-gun Enterprise-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was built during the American War of Independence and serving during the later years of that conflict. She continued to serve during the years of peace and had an active career during the French Revolutionary Wars and most of the Napoleonic Wars, until being broken up in 1814.

HMS Mercury cutting out a French gunboat from Rovigno, 1 April 1809
HMS Amphion was a 32-gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She served during the Napoleonic Wars.
Amphion was built by Betts, of Mistleythorn, and was launched on 19 March 1798.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Spartan_(1806)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Mercury_(1779)

HMS Amphion (1798) - Wikipedia
1811 – Launch of HMS Investigator was a survey brig of the Royal Navy
HMS Investigator was a survey brig of the Royal Navy. She performed surveying duties until she was paid off in 1835. She then became a police ship moored on the Thames River. she was broken up in 1857.

Scale: 1:48. Plan showing the body plan with stern board detail, sheer lines with inboard detail, and longitudinal half-breadth for building the Investigator (1811) as a 6-gun Survey Vessel. Signed Henry Peake [Surveyor of the Navy, 1806-1822]
HMS Investigator (1811) - Wikipedia
1839 – Death of Jacques Félix Emmanuel Hamelin, French admiral and explorer (b. 1768)
Baron Jacques Félix Emmanuel Hamelin (13 October 1768 – 23 April 1839) was a rear admiral of the French navy and later a Baron. He commanded numerous naval expeditions and battles with the British Navy as well as exploratory voyages in the Indian Ocean and the South Seas.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jacques_Félix_Emmanuel_Hamelin
1889 – Birth of Karel Doorman, Dutch admiral (d. 1942)
Karel Willem Frederik Marie Doorman (23 April 1889 – 28 February 1942) was a Dutch naval officer who during World War II commanded remnants of the short-lived American-British-Dutch-Australian Commandnaval strike forces in the Battle of the Java Sea. He was killed in action when his flagship HNLMS De Ruyter was torpedoed during the battle, having chosen to go down with the ship.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karel_Doorman
1945 – The Action of 23 April 1945 was a submarine engagement of World War II that occurred in the Java Sea between Nazi Germany and the United States. USS Besugo (SS 321) sinks the German submarine U 183 in the Java Sea.
The Action of 23 April 1945 was a submarine engagement of World War II that occurred in the Java Sea between Nazi Germany and the United States. It resulted in the last sinking of a German U-boat in Asian waters during the Pacific War and was one of only a few actions of the theater involving German forces.
USS Besugo, under the command of Lieutenant Commander Herman Edward Miller, made radar contact with U-183 at about 01:00 off the southern coast of Borneo while patrolling the area. Underwater, the Americans fired a spread of torpedoes and one struck the U-boat which had a Japanese flag painted on the side. The German submarine sank quickly at position 04°50′S 112°52′E with 54 men still aboard, including Kapitänleutnant (Lieutenant Commander) Fritz Schneewind. Afterward, the Americans surfaced and rescued one wounded German warrant officer and took him prisoner.






 soon trickled in of the repulse of the galleys and the governor extended gifts upon them and granted them stay for as long as they wanted. After around four days and with the wind now in their favor, the English sailed off without incident; the Spanish in the harbor of Algeciras unable to intercept them because of their severe damage or the rough sea. The English soon arrived off the coast of England without further hindrance.
soon trickled in of the repulse of the galleys and the governor extended gifts upon them and granted them stay for as long as they wanted. After around four days and with the wind now in their favor, the English sailed off without incident; the Spanish in the harbor of Algeciras unable to intercept them because of their severe damage or the rough sea. The English soon arrived off the coast of England without further hindrance.