Today in Naval History - Naval / Maritime Events in History
Other Events on 20 May
1497 – John Cabot sets sail from Bristol, England, on his ship Matthew looking for a route to the west (other documents give a May 2 date).
John Cabot (Italian: Giovanni Caboto [dʒoˈvanni kaˈbɔːto]; c. 1450 – c. 1500) was an Italian navigator and explorer. His 1497 discovery of the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England is the earliest known European exploration of coastal North America since the Norse visits to Vinland in the eleventh century. To mark the celebration of the 500th anniversary of Cabot's expedition, both the Canadian and British governments elected Cape Bonavista, Newfoundland, as representing Cabot's first landing site. However, alternative locations have also been proposed.


Route of 1497 voyage posited by Jones and Condon.

A replica of the Matthew in Bristol
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Cabot
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matthew_(ship)
1498 – Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama discovers the sea route to India when he arrives at Kozhikode (previously known as Calicut), India.
The discovery of the sea route to India was the first recorded trip made directly from Europe to India via the Atlantic Ocean. It was undertaken under the command of Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama during the reign of King Manuel I in 1495–1499. Considered to be one of the most remarkable voyages of the Age of Discovery, it consolidated the Portuguese maritime presence over the Indian Ocean and that country's dominance of global trade routes

Vasco da Gama on his arrival in India, bearing the flag used during the first voyage by sea to this part of the world: the arms of Portugal and the Cross of the Order of Christ, sponsors of the expansion movement initiated by Henry the Navigator, are seen. Painting by Ernesto Casanova
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portuguese_discovery_of_the_sea_route_to_India
1666 - Undecided encounter between an English and a combined Dutch\French squadron at the isle of Nevis
1780 – Launch of HMS Daedalus, a 32-gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy, launched in 1780 from the yards of John Fisher, of Liverpool.
HMS Daedalus was a 32-gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy, launched in 1780 from the yards of John Fisher, of Liverpool. She went on to serve in the American War of Independence, as well as the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Daedalus_(1780)
1799 – End of Siege of Acre of 1799 was an unsuccessful French siege of the Ottoman-defended, walled city of Acre (now Akko in modern Israel) and was the turning point of Napoleon's invasion of Egypt and Syria.
It was Napoleon`s first strategic defeat as three years previously he had been tactically defeated at the Second Battle of Bassano.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Siege_of_Acre_(1799)
https://threedecks.org/index.php?display_type=show_battle&id=649
1801 Four US warships sent to Mediterranean to protect American commerce under Commodore Richard Dale
1806 – Launch of French Élisa, a Pallas class constituted the standard design of 40-gun frigates of the French Navy during the Napoleonic Empire period.

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
1814 – Launch of HMS Tyne, a Conway class sailing sixth rates were a series of ten Royal Navy post ships built to an 1812 design by Sir William Rule
The Conway class sailing sixth rates were a series of ten Royal Navy post ships built to an 1812 design by Sir William Rule. All ten were ordered on 18 January 1812, and nine of these were launched during 1814, at the end of the Napoleonic War; the last (Tees) was delayed and was launched in 1817.
These ships were originally designated as "sloops", but were nominally rated as sixth rates of 20 guns when built, as their 12-pounder carronades were not included in the official rating. When this changed in February 1817, they were rated at 28 guns.

Scale 1:48. Plan showing the body plan, sheer lines and longitudinal half breadth proposed and approved, for Fowey / Towey (1814), Mersey (1814), Conway (1814), Eden (1814), Tyne (1814), Tanmar (1814), Tees (1817), Menai (1814), Wye (1814), Dee (1814), all 26/28-gun Sloops to be built by contract in private yards. Note alterations to back stay, main channel, fore channel and hawse pipes for Tamar in 1817. Annotation at top: "Chatham Officers were directed to fit the fore backstay stool further aft and Mizzien backstay stool 3ft further aft, on board the Tamar, and to fit her with Trysail Mast Pr Warrant dated 26 February 17."
 en.wikipedia.org
https://collections.rmg.co.uk/colle...el-355971;browseBy=vessel;vesselFacetLetter=T
en.wikipedia.org
https://collections.rmg.co.uk/colle...el-355971;browseBy=vessel;vesselFacetLetter=T
1855 – Launch of French Arcole, a 90-gun Algésiras-class steam ship of the line of the French Navy
The Arcole was a 90-gun Algésiras-class steam ship of the line of the French Navy.
Arcole was the second of production ship built on the principles of the "fast ship of the line" pioneered by Napoléon. She took the place of the 130-gun Desaix, of the Bretagne type, when the latter was cancelled.
She took part in the Second Italian War of Independence, and was broken up in 1872.

The Algésiras class was a late type of 90-gun ships of the line used by the French navy. They were designed from the beginning to use a combination of sail and steam engine for propulsion.
After the breakthrough of the Napoléon, the Algésiras class was the improved designed which went into mass production.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/French_ship_Arcole_(1855)

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
1886 – Launch of Ekaterina II (Russian: Екатерина II Catherine II of Russia) was the lead ship of the Ekaterina II-class pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the 1880s.
Ekaterina II (Russian: Екатерина II Catherine II of Russia) was the lead ship of the Ekaterina II-class pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the 1880s. Her crew was considered unreliable when the crew of the battleship Potemkin mutinied in June 1905 and her engines were decoupled from the propellers to prevent her from joining Potemkin. She was turned over to the Sevastopol port authorities before being stricken on 14 August 1907. She was re-designated as Stricken Vessel Nr. 3 on 22 April 1912 before being sunk as a torpedo target for the Black Sea Fleet.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Russian_battleship_Ekaterina_II

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
1901 – Launch of HMS Euryalus, a Cressy-class armoured cruiser built for the Royal Navy around 1900
HMS Euryalus was a Cressy-class armoured cruiser built for the Royal Navy around 1900. Badly damaged by multiple accidents while fitting out, she was not completed until 1904. She became flagship of the Australia Station that year and was reduced to reserve upon her return in 1905. Recommissioned in 1906, she became a training ship for the North America and West Indies Station before being placed in reserve with the Third Fleet in 1909.

Recommissioned at the start of World War I, Euryalus was assigned to the 7th Cruiser Squadron. She became flagship of the Southern Force defending the eastern end of the English Channel from any German attack, shortly after the war began. She was present at the Battle of Heligoland Bight a few weeks after the war began, but saw no combat. She was transferred to convoy escort duties in the Bay of Biscay in late 1914, before being sent to Egypt in early 1915. Euryalus was then assigned to support British troops during the Gallipoli Campaign by providing naval gunfire. She covered the landing at Cape Helles in April as well as providing fire support during one subsequent British offensive. She became the flagship of the East Indies Station in January 1916, until relieved in July 1917. Later that year she began a conversion into a minelayer at Hong Kong, but this was still incomplete when the war ended. Euryalus returned home in 1919 and was sold for scrap the following year.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Euryalus_(1901)

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
1902 – Launch of Komintern, a Soviet light cruiser originally named Pamiat' Merkuria (Memory of Mercury), a Bogatyr-class protected cruiser built for the Imperial Russian Navy.
Komintern was a Soviet light cruiser originally named Pamiat' Merkuria (Memory of Mercury), a Bogatyr-class protected cruiser built for the Imperial Russian Navy. She saw service during World War I in the Black Sea and survived the Russian Civil War, although heavily damaged. She was repaired by the Soviet Navy and put into service as a training cruiser. In 1941 she was reclassified as a minelayer and provided gunfire support and transported troops during the Siege of Odessa, Siege of Sevastopol, and the Kerch-Feodosiya Operation in the winter of 1941—42. She was damaged beyond repair at Poti by a German air attack on 16 July 1942. Afterwards she was disarmed and hulked. At some point she was towed to the mouth of the Khobi river and sunk there as a breakwater on 10 October 1942.


Komintern under repair in 1923
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Soviet_cruiser_Komintern
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bogatyr-class_cruiser
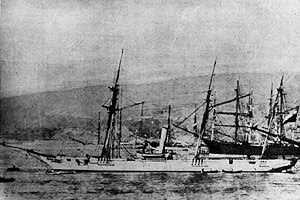
1907 - SS Izaro was a Spanish steamship that had been wrecked in 1907
SS Izaro was a Spanish steamship that had been wrecked in 1907.
Izaro was on her way to Maryport, Cumbria, England, with a cargo of iron ore when she ran aground on Tomlin Rocks at St Bees, Cumbria, on 20 May 1907. The crew scrambled to safety, but the ship was stuck fast, with bow and stern on the rocks, but her midships unsupported. The weight of her cargo caused her to split in two. The cargo was salvaged, but the ship was a total loss. As much of the ship′s ironwork as possible was salvaged, and the remainder was dragged out to sea. The remains of her boilers and keel can still be seen.

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
1917 - HMS Paxton – British Q-ship sunk by German submarine U-46 on 20 May 1917 off the West coast of Ireland.
HMS Paxton was a First World War Royal Navy Q-Ship torpedoed and sunk by the German submarine U-46 on 20 May 1917 in the Atlantic Ocean 90 miles west of Great Skellig, Eire. The ship was originally ordered as Lady Patricia for the British and Irish Steam Packet Company but taken over on completion by the British Government as HMAV Lady Patricia.
The ship was damaged by gunfire from the German submarine U-57 on 30 March 1917 in St George's Channel and six crew killed. Shortly afterwards work started on converting her to an anti-submarine Q-ship, Q25, which was completed on 30 April 1917. The ship was commissioned as HMS Paxton the following day and sunk less than three weeks later.
Sinking
At about 9:00 on 20 May 1917 the ship was heading west at about 8 knots when an unknown German submarine surfaced and shelled her with its deck gun, hitting the ship once. Paxton responded by firing back at the submarine with her stern 4 inch gun, thus revealing herself as a Q-Ship. The submarine dived to escape.
Paxton continued on her westerly course, and the crew changed her disguise by painting the name of a Swedish ship on her sides. At 19:15 on the same day U-46 torpedoed her, disabling the engines. Two men were killed, including the chief engineer, but the ship remained afloat because she was loaded with lumber. The submarine fired a second torpedo fifteen minutes later which broke the ship's back and it sank within about five minutes. The surviving crew abandoned the ship on two boats and two rafts, but had not been able to send a distress radio message. The submarine surfaced and took the captain, Commander George Hewett and the second engineer, Engineer Sub-Lieutenant James Wilfred Johnson prisoner.
The boats and rafts stayed together overnight, but at 5 am one boat separated to make for Berehaven (now Castletownbere) for help. The boat had no food or water onboard. However it was spotted just after 9 pm, by an American destroyer, USS Wadsworth, which rescued the three officers and eight ratings on it but despite spending the following day searching the destroyer could not locate the other survivors. On 26 May a further four crew were rescued from a raft by another ship, and on 26 or 27 May the second boat, containing the remaining survivors reached Killybegs. Provisions and water had run out four days before the boat arrived, and two people had died en route. In all 31 people were killed.
Surgeon Sub-Lieutenant Annesley George Lennon Brown, RNVR was awarded the Distinguished Service Cross in June 1919 for his gallantry and devotion to duty following the torpedoing.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Paxton
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SM_U-46
1939 – Launch of Chūyō (冲鷹, "hawk which soars") was a Taiyō-class escort carrier originally built as Nitta Maru (新田 丸), the first of her class of three passenger-cargo liners built in Japan during the late 1930s.
Chūyō (冲鷹, "hawk which soars") was a Taiyō-class escort carrier originally built as Nitta Maru (新田 丸), the first of her class of three passenger-cargo liners built in Japan during the late 1930s. She was requisitioned by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in late 1941 and was converted into an escort carrier in 1942. She spent most of her service ferrying aircraft, cargo and passengers to Truk until she was torpedoed and sunk by an American submarine in late 1943 with heavy loss of life.


https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Japanese_aircraft_carrier_Chūyō
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taiyō-class_escort_carrier
1943 - The Tenth Fleet is established in Washington D.C., under the command of Adm. Ernest J. King, to coordinate U.S. anti-submarine operations in the Atlantic. Disbanded after WWII, the Tenth Fleet is reactivated in Jan. 2010 as U.S. Fleet Cyber Command.
1944 - USS Angler (SS 240) sinks Japanese transport Otori Maru and survives depth charging by its escort, while both USS Silversides (SS 236) and USS Bluegill (SS 242) sink enemy vessels.
Other Events on 20 May
1497 – John Cabot sets sail from Bristol, England, on his ship Matthew looking for a route to the west (other documents give a May 2 date).
John Cabot (Italian: Giovanni Caboto [dʒoˈvanni kaˈbɔːto]; c. 1450 – c. 1500) was an Italian navigator and explorer. His 1497 discovery of the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England is the earliest known European exploration of coastal North America since the Norse visits to Vinland in the eleventh century. To mark the celebration of the 500th anniversary of Cabot's expedition, both the Canadian and British governments elected Cape Bonavista, Newfoundland, as representing Cabot's first landing site. However, alternative locations have also been proposed.


Route of 1497 voyage posited by Jones and Condon.

A replica of the Matthew in Bristol
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Cabot
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matthew_(ship)
1498 – Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama discovers the sea route to India when he arrives at Kozhikode (previously known as Calicut), India.
The discovery of the sea route to India was the first recorded trip made directly from Europe to India via the Atlantic Ocean. It was undertaken under the command of Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama during the reign of King Manuel I in 1495–1499. Considered to be one of the most remarkable voyages of the Age of Discovery, it consolidated the Portuguese maritime presence over the Indian Ocean and that country's dominance of global trade routes

Vasco da Gama on his arrival in India, bearing the flag used during the first voyage by sea to this part of the world: the arms of Portugal and the Cross of the Order of Christ, sponsors of the expansion movement initiated by Henry the Navigator, are seen. Painting by Ernesto Casanova
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portuguese_discovery_of_the_sea_route_to_India
1666 - Undecided encounter between an English and a combined Dutch\French squadron at the isle of Nevis
1780 – Launch of HMS Daedalus, a 32-gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy, launched in 1780 from the yards of John Fisher, of Liverpool.
HMS Daedalus was a 32-gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy, launched in 1780 from the yards of John Fisher, of Liverpool. She went on to serve in the American War of Independence, as well as the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Daedalus_(1780)
1799 – End of Siege of Acre of 1799 was an unsuccessful French siege of the Ottoman-defended, walled city of Acre (now Akko in modern Israel) and was the turning point of Napoleon's invasion of Egypt and Syria.
It was Napoleon`s first strategic defeat as three years previously he had been tactically defeated at the Second Battle of Bassano.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Siege_of_Acre_(1799)
https://threedecks.org/index.php?display_type=show_battle&id=649
1801 Four US warships sent to Mediterranean to protect American commerce under Commodore Richard Dale
1806 – Launch of French Élisa, a Pallas class constituted the standard design of 40-gun frigates of the French Navy during the Napoleonic Empire period.

Pallas-class frigate (1808) - Wikipedia
1814 – Launch of HMS Tyne, a Conway class sailing sixth rates were a series of ten Royal Navy post ships built to an 1812 design by Sir William Rule
The Conway class sailing sixth rates were a series of ten Royal Navy post ships built to an 1812 design by Sir William Rule. All ten were ordered on 18 January 1812, and nine of these were launched during 1814, at the end of the Napoleonic War; the last (Tees) was delayed and was launched in 1817.
These ships were originally designated as "sloops", but were nominally rated as sixth rates of 20 guns when built, as their 12-pounder carronades were not included in the official rating. When this changed in February 1817, they were rated at 28 guns.

Scale 1:48. Plan showing the body plan, sheer lines and longitudinal half breadth proposed and approved, for Fowey / Towey (1814), Mersey (1814), Conway (1814), Eden (1814), Tyne (1814), Tanmar (1814), Tees (1817), Menai (1814), Wye (1814), Dee (1814), all 26/28-gun Sloops to be built by contract in private yards. Note alterations to back stay, main channel, fore channel and hawse pipes for Tamar in 1817. Annotation at top: "Chatham Officers were directed to fit the fore backstay stool further aft and Mizzien backstay stool 3ft further aft, on board the Tamar, and to fit her with Trysail Mast Pr Warrant dated 26 February 17."
Conway-class post ship - Wikipedia
1855 – Launch of French Arcole, a 90-gun Algésiras-class steam ship of the line of the French Navy
The Arcole was a 90-gun Algésiras-class steam ship of the line of the French Navy.
Arcole was the second of production ship built on the principles of the "fast ship of the line" pioneered by Napoléon. She took the place of the 130-gun Desaix, of the Bretagne type, when the latter was cancelled.
She took part in the Second Italian War of Independence, and was broken up in 1872.

The Algésiras class was a late type of 90-gun ships of the line used by the French navy. They were designed from the beginning to use a combination of sail and steam engine for propulsion.
After the breakthrough of the Napoléon, the Algésiras class was the improved designed which went into mass production.
- Algésiras 1855
- Arcole 1855
- Impérial 1856
- Intrépide 1864
- Redoutable 1857
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/French_ship_Arcole_(1855)

Algésiras-class ship of the line - Wikipedia
1886 – Launch of Ekaterina II (Russian: Екатерина II Catherine II of Russia) was the lead ship of the Ekaterina II-class pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the 1880s.
Ekaterina II (Russian: Екатерина II Catherine II of Russia) was the lead ship of the Ekaterina II-class pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the 1880s. Her crew was considered unreliable when the crew of the battleship Potemkin mutinied in June 1905 and her engines were decoupled from the propellers to prevent her from joining Potemkin. She was turned over to the Sevastopol port authorities before being stricken on 14 August 1907. She was re-designated as Stricken Vessel Nr. 3 on 22 April 1912 before being sunk as a torpedo target for the Black Sea Fleet.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Russian_battleship_Ekaterina_II

Ekaterina II-class battleship - Wikipedia
1901 – Launch of HMS Euryalus, a Cressy-class armoured cruiser built for the Royal Navy around 1900
HMS Euryalus was a Cressy-class armoured cruiser built for the Royal Navy around 1900. Badly damaged by multiple accidents while fitting out, she was not completed until 1904. She became flagship of the Australia Station that year and was reduced to reserve upon her return in 1905. Recommissioned in 1906, she became a training ship for the North America and West Indies Station before being placed in reserve with the Third Fleet in 1909.

Recommissioned at the start of World War I, Euryalus was assigned to the 7th Cruiser Squadron. She became flagship of the Southern Force defending the eastern end of the English Channel from any German attack, shortly after the war began. She was present at the Battle of Heligoland Bight a few weeks after the war began, but saw no combat. She was transferred to convoy escort duties in the Bay of Biscay in late 1914, before being sent to Egypt in early 1915. Euryalus was then assigned to support British troops during the Gallipoli Campaign by providing naval gunfire. She covered the landing at Cape Helles in April as well as providing fire support during one subsequent British offensive. She became the flagship of the East Indies Station in January 1916, until relieved in July 1917. Later that year she began a conversion into a minelayer at Hong Kong, but this was still incomplete when the war ended. Euryalus returned home in 1919 and was sold for scrap the following year.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Euryalus_(1901)

Cressy-class cruiser - Wikipedia
1902 – Launch of Komintern, a Soviet light cruiser originally named Pamiat' Merkuria (Memory of Mercury), a Bogatyr-class protected cruiser built for the Imperial Russian Navy.
Komintern was a Soviet light cruiser originally named Pamiat' Merkuria (Memory of Mercury), a Bogatyr-class protected cruiser built for the Imperial Russian Navy. She saw service during World War I in the Black Sea and survived the Russian Civil War, although heavily damaged. She was repaired by the Soviet Navy and put into service as a training cruiser. In 1941 she was reclassified as a minelayer and provided gunfire support and transported troops during the Siege of Odessa, Siege of Sevastopol, and the Kerch-Feodosiya Operation in the winter of 1941—42. She was damaged beyond repair at Poti by a German air attack on 16 July 1942. Afterwards she was disarmed and hulked. At some point she was towed to the mouth of the Khobi river and sunk there as a breakwater on 10 October 1942.


Komintern under repair in 1923
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Soviet_cruiser_Komintern
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bogatyr-class_cruiser
1907 - SS Izaro was a Spanish steamship that had been wrecked in 1907
SS Izaro was a Spanish steamship that had been wrecked in 1907.
Izaro was on her way to Maryport, Cumbria, England, with a cargo of iron ore when she ran aground on Tomlin Rocks at St Bees, Cumbria, on 20 May 1907. The crew scrambled to safety, but the ship was stuck fast, with bow and stern on the rocks, but her midships unsupported. The weight of her cargo caused her to split in two. The cargo was salvaged, but the ship was a total loss. As much of the ship′s ironwork as possible was salvaged, and the remainder was dragged out to sea. The remains of her boilers and keel can still be seen.

SS Izaro - Wikipedia
1917 - HMS Paxton – British Q-ship sunk by German submarine U-46 on 20 May 1917 off the West coast of Ireland.
HMS Paxton was a First World War Royal Navy Q-Ship torpedoed and sunk by the German submarine U-46 on 20 May 1917 in the Atlantic Ocean 90 miles west of Great Skellig, Eire. The ship was originally ordered as Lady Patricia for the British and Irish Steam Packet Company but taken over on completion by the British Government as HMAV Lady Patricia.
The ship was damaged by gunfire from the German submarine U-57 on 30 March 1917 in St George's Channel and six crew killed. Shortly afterwards work started on converting her to an anti-submarine Q-ship, Q25, which was completed on 30 April 1917. The ship was commissioned as HMS Paxton the following day and sunk less than three weeks later.
Sinking
At about 9:00 on 20 May 1917 the ship was heading west at about 8 knots when an unknown German submarine surfaced and shelled her with its deck gun, hitting the ship once. Paxton responded by firing back at the submarine with her stern 4 inch gun, thus revealing herself as a Q-Ship. The submarine dived to escape.
Paxton continued on her westerly course, and the crew changed her disguise by painting the name of a Swedish ship on her sides. At 19:15 on the same day U-46 torpedoed her, disabling the engines. Two men were killed, including the chief engineer, but the ship remained afloat because she was loaded with lumber. The submarine fired a second torpedo fifteen minutes later which broke the ship's back and it sank within about five minutes. The surviving crew abandoned the ship on two boats and two rafts, but had not been able to send a distress radio message. The submarine surfaced and took the captain, Commander George Hewett and the second engineer, Engineer Sub-Lieutenant James Wilfred Johnson prisoner.
The boats and rafts stayed together overnight, but at 5 am one boat separated to make for Berehaven (now Castletownbere) for help. The boat had no food or water onboard. However it was spotted just after 9 pm, by an American destroyer, USS Wadsworth, which rescued the three officers and eight ratings on it but despite spending the following day searching the destroyer could not locate the other survivors. On 26 May a further four crew were rescued from a raft by another ship, and on 26 or 27 May the second boat, containing the remaining survivors reached Killybegs. Provisions and water had run out four days before the boat arrived, and two people had died en route. In all 31 people were killed.
Surgeon Sub-Lieutenant Annesley George Lennon Brown, RNVR was awarded the Distinguished Service Cross in June 1919 for his gallantry and devotion to duty following the torpedoing.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Paxton
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SM_U-46
1939 – Launch of Chūyō (冲鷹, "hawk which soars") was a Taiyō-class escort carrier originally built as Nitta Maru (新田 丸), the first of her class of three passenger-cargo liners built in Japan during the late 1930s.
Chūyō (冲鷹, "hawk which soars") was a Taiyō-class escort carrier originally built as Nitta Maru (新田 丸), the first of her class of three passenger-cargo liners built in Japan during the late 1930s. She was requisitioned by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in late 1941 and was converted into an escort carrier in 1942. She spent most of her service ferrying aircraft, cargo and passengers to Truk until she was torpedoed and sunk by an American submarine in late 1943 with heavy loss of life.


https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Japanese_aircraft_carrier_Chūyō
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taiyō-class_escort_carrier
1943 - The Tenth Fleet is established in Washington D.C., under the command of Adm. Ernest J. King, to coordinate U.S. anti-submarine operations in the Atlantic. Disbanded after WWII, the Tenth Fleet is reactivated in Jan. 2010 as U.S. Fleet Cyber Command.
1944 - USS Angler (SS 240) sinks Japanese transport Otori Maru and survives depth charging by its escort, while both USS Silversides (SS 236) and USS Bluegill (SS 242) sink enemy vessels.